i-How: Science - How does fractional distilation of crude oil work?
When crude oil reaches the oil refinery it is a thick black, smelly liquid.
In this form, it is not much use to anyone. Crude oil contains mixture of hydrocarbons.
At the refinery these are separated
into fractions which are more useful.
This is done by a process called fractional distillation. This process separates compounds by using the difference
in boiling points. See diagram below. A
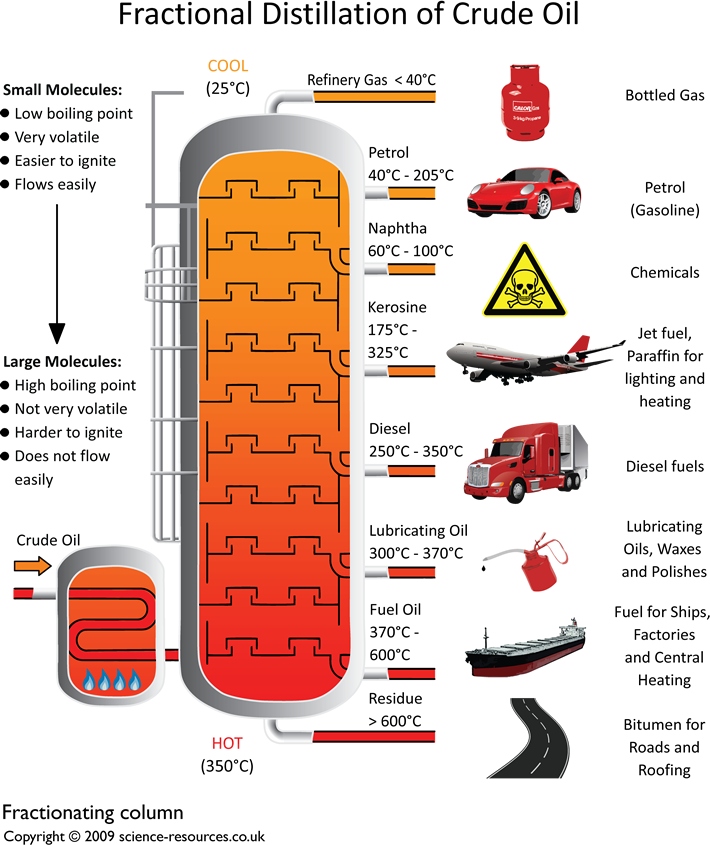
Fractionating Column Picture: Yokkaichi oil refinery, Mie Prefecture, Japan Separation of crude oil: Image courtesy of science-resources.co.uk Click here to download an A3 printable version of this. Crude oil enters the fractionating column as gas.
The column is quite hot at the bottom and cooler at the top.
This difference in the temperature up and down the column sorts the
different fractions from each other. The larger hydrocarbons,
with the high boiling points, turn back into
liquids at the base of the column and the smaller
hydrocarbons stay as gases.
They rise up the column and condense at different levels, as shown in the above diagram. At
the top of the column there are a number of hydrocarbons with low boiling points - between
20ºC and 70ºC. These remain as gases. The discovery of the the crude oil has
played a very big part in the development of modern life. It provides
the fuel for most of today's transport as well as the raw material for making
various chemical like PLASTICS. There are a few things
you must know about hydrocarbons!
How fractional distillation of crude oil works:

The boiling
point increases Becomes less flamable Becomes more
viscous Becomes less
volatile Gets less volatile (doesn't evaporate so easily). As the size of the hydrocarbon molecule increases:






![]()
Tags:Hydrocarbons, Cracking, Petrol, Ethane, Molecules, Diesel, Alkenes, Catalyst, Crude oil, Fractional distillation, Viscosity, how is crude oil separated, crude oil separation process, how to separate crude oil, separation of crude oil, crude oil separation, industrial distillation column, industrial distillation, fractional distillation of crude oil GCSE, how does fractional distillation of crude oil work, what is crude oil a mixture of, tray distillation column, distillation column trays, sieve tray distillation column, industrial distillation column, oil distillation column, how does fractional distillation of crude oil work, distillation column efficiency, distillation column control